Treatment of child malnutrition
Malnutrition refers to the presence of deficiencies, defects, or some excesses in a person’s consumption of energy and nutrients. The term malnutrition covers two groups of cases, one of which is a lack of nutrition,
These include stunting (short height for age),
wasting (low weight for height), weight loss (low weight for age), micronutrient deficiency (lack of important vitamins and minerals), and the other group is overweight, obesity, and noncommunicable diseases associated with the diet,
Such as heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and cancer. Malnutrition affects many people in every country. About 1.9 billion adults worldwide are overweight, compared to 462 million who are underweight, and an estimated 41 million children under 5 years of age are overweight. Or obesity, while about 159 million are stunted, in addition to that, 528 million or approximately 29% of women of childbearing age worldwide have anemia.
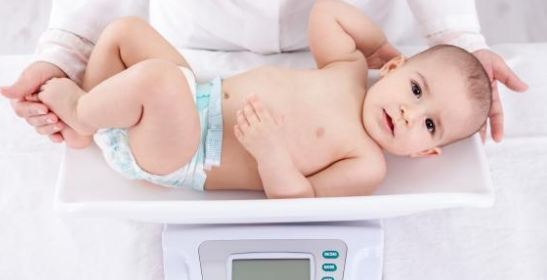
Treatment of child malnutrition
Child malnutrition often occurs as a result of long-term health conditions, which are often needed in hospital treatment, but this may not apply to all malnourished children, so malnutrition treatment may include the following:
Dietary changes, such as eating foods rich in energy and nutrients, are the most important tips: a healthy, balanced diet. Eat fortified foods, which contain additional nutrients.
Eat nutritious snacks between main meals. Drink a lot of calories. Supporting families to control the basic factors that affect a child’s nutritional intake. Treating any underlying medical condition that may cause malnutrition. Take vitamin and mineral supplements.
Take energy-rich and protein supplements if other treatments aren’t enough on their own. Children with severe malnutrition need to be fed and nurtured very carefully, so they may not be given a normal diet immediately but usually need special care in the hospital, and after improvement they can gradually return to a regular or normal diet and continue to do so at home, It is important to monitor the treatment regularly to ensure that it is suitable for the child, as regular measurements are made of weight and height, with reference to specialized services if no improvement appears.
For people who cannot eat enough food to meet the needs of their bodies, such as those who have trouble swallowing, an alternative method of obtaining nutrients may be needed, and these methods may include the following:
Food tube from the nose to the stomach. A tube placed directly in the stomach or gut through the skin of the abdomen. A solution containing nutrients given directly into the blood through a tube placed in a vein, in what is known as intravenous nutrition. These treatments usually start first in the hospital, and can continue at home if the person is in good condition.









sale isotretinoin roacutan website cheapeast
Cialis Und Priligy
cialis pharmacie ligne
Viagra Delle Donne
Forum Acquisto Viagra Generico
Comprar Cialis Medicamento
Kamagra In Canada
Que Es Cialis 20 Mg
Pill Identifier Amoxicillin 500
Cash On Delivery Acticin Tab Usa Overseas Without Dr Approval
Viagra Sous La Langue
cheapest kamagra in uk
Pharmacie En Ligne Pour Propecia
cialis pharmacie ligne
Farmaci Con Dapoxetina
Vitamins That Work With Amoxicillin
Comparatif Viagra Generique Levitra
cialis from canadian pharmacy
Amoxil Dosage
Amoxicillin With Clavulanic Acid And Chewable